In the staffing industry, what two things can you do to reduce turnover?

Quick links
-
Introduction
-
#1- Work history, work history, work history
-
#2- Document Applicant Feedback
-
How UZIO Can Help?
-
Get in Touch with us for an expert-led demo
Introduction
Especially in these current market conditions, you deserve credit for what you do every day. You fight unemployment claims, create plans to lower turnover rates, challenge fraudulent injury claims, test ways to get walk in traffic, try to figure out why job board prices are skyrocketing, and continually keep company morale as high as possible. This does not even include the battles you fight with competitors!
While there may not be total solutions to all of these challenges, there are some solutions that can help and also free up your valuable time so you can create an action plan that will not only help you survive but even thrive.
Here’s two tips we believe is critical for staffing companies:
#1- Work history, work history, work history
Every vendor in the marketplace is trying to find ways to save you time and assist with job exposure. Job boards are creating aptitude and personality tests. New companies are forming everyday that include referral programs all the way down to surveys. You may have been contacted by vendors telling you to invest in company reputation systems.
All of these can be great and extremely helpful however, none can replace the most important thing for your recruiters in today’s job climate. Work history should be the top priority for anyone deciding on placements. Especially in the light industrial sector, this will directly impact your turnover percentage with each client. A recruiter verifying and confirming work history will outperform another recruiter using any other system that does not include the same.
As simple as this sounds, many staffing companies are not emphasizing this to their recruiters. It’s easy to worry about ATS activity and filling in the blanks but there is a reason you exist. You fill job orders with the best possible applicants. At UZIO, we recommend you ask every applicant to go back a minimum of five years. Even if they cannot provide employment for all five years, at least make applicants provide you with the what and why since 2017.
We are slowly trending back to pre-Covid work conditions. Your turnover rate will continue to become more important in rating your service versus competitors. We challenge you to review some of your placements and find how many have job history (or reasons for no history) completely documented.
#2- Document Applicant Feedback
A simple task but unfortunately, not as common as you think with recruiters. Many perform exit interviews but few log the exact reasons for applicants turning down assignments. Understandably, they must contact more applicants than ever to fill openings; however, the documentation still needs to happen.
Many of your contacts you work with do not make the final decision with pay rates. Most have their own bosses who they go through to make that decision. Also, most of your contacts probably agree they should pay more but they don’t think they can get the approval. What will assist your contact more: informing them that a bunch of applicants said they need more money or a file with specific names, dates, minimum pay rates, and additional comments.
How UZIO Can Help?
UZIO is the all-in-one platform to help you get rid of operational inefficiencies due to siloed business applications and help you reach your full potential across payroll, HR, time tracking and billing. It is the only solution you will need to run your business.
While working with clients and addressing their challenges, we have come to know the staffing industry. We have discovered that our platform integrates well with staffing companies and offers solutions that out-perform our competitors.
We would love to have an initial conversation with no strings attached. Let us discuss or explain what we can offer. Please click here to schedule a discussion.
Payroll Trends: What’s the Future of Payroll look like in the upcoming years

Quick links
-
Introduction
-
Standalone Vs All-in-one Payroll System
-
Innovative and Flexible Payment Options
-
Compliance Challenges
-
Gig Economy and Lack of Benefits
-
Conclusion
Introduction
If you are part of the 29% of SMBs using an older payroll systems, you’re in luck. Thanks to recent optimization of payroll service offerings, there’s a lot of cool features in HRIS and payroll services that will reduce time consuming and eliminate manual processes. Check out how payroll services are changing how embracing AI, accommodating the growing gig economy, reducing the complexity of remaining in compliance and more…
A recent study by Kronos and the American Payroll Association has found that 29% of SMBs use an outdated payroll process. Many are using spreadsheets and other manual payroll processes. If you are in this group, it may be time for a payroll process upgrade. Here’s some interesting trends occurring in the payroll industry.
Standalone Vs All-in-one Payroll System
Standalone payroll systems are a thing of the past – All-in-one payroll solutions like UZIO are the way to go. Designed to reduce or eliminate manual processes, these all-in-one solutions create an easy to use, self-service environment enabling businesses to be able to manage all their payroll functions without any assistance. This helps reduce business reliance on support heavy payroll services or vendor support.
Innovative and Flexible Payment Options
Flexible payment options change how employees get paid – As payroll processing is increasingly digitized, diverse compensation administration options are becoming a must have. Not only are the standard paper checks versus direct deposit a current feature expectation, other employee payment options are emerging. An employee payment self-service option is an attractive feature. Crypto currency payments may become more widespread in use as this payment method becomes more popular. According to a recent Statista report, over 39% of surveyed Americans reported they would be “open to the idea of using Bitcoin for transactions and purchases.”
Artificial Intelligence (AI) automates and optimizes payroll processes – Payroll systems will be able to continue to learn and anticipate what employees want from payroll. This is thanks to AI enhancements that are built into payroll software solutions. AI will enable payroll systems to automate processes, increase efficiency and reduce errors. Want to learn more about how AI is being leveraged, check out this recent article by Forbes “11 Ways AI Can Revolutionize Human Resources.”
Compliance Challenges
Compliance can become a bit less daunting – The changing landscape of financial laws and regulations will require constant diligence. As AI is increasingly built into payroll systems, it can help automate compliance. AI can help with real-time updating of tax, wage rates and any applicable changing laws.
Gig Economy and Lack of Benefits
Gig economy growth requires changing benefit offerings – The growth of the gig economy is becoming more of the norm. Payroll services will need to adapt and provide the appropriate support for these non-traditional workers. For many non-traditional workers, any health benefits have not been provided. According to CNN Business reports, “Millions of American workers don’t have access to health insurance through an employer.”
Conclusion
Trends suggest payroll providers will need to develop the appropriate accommodation to these unique needs of this currently underserved area. Only those payroll system providers who are able understand and adapt to the changing demand will be able to survive and grow at a rapid pace.
When is the right time to leave a PEO?

Quick links
-
Introduction
-
Medical benefits with PEO
-
PEO Customer Service
-
PEO Fees
-
Things to consider when transitioning out of a PEO
-
Best time to leave a PEO
-
Conclusion
Introduction
The chances are when you were starting out, you wanted to focus on getting your business off the ground and not on day-to-day HR issues so you decided to outsource your HR functions to a PEO.
Now you are a growing company, your headcount has gone up, maybe north of 50 employees. You are seeing the cost of the PEO going up and their service may be stagnating or reversing. You are wondering is it the right time to leave the PEO and bring your HR function in-house?
There is not an easy answer to this question because things vary so much from one company to another. In this article, we will provide you a framework you can use to make this decision.
The decision to leave the PEO will come down to your decision with respect to the following three major items:
- Providing Medical Benefits to your employees
- PEO Customer service
- PEO Fees
Medical benefits
One of the important advantages which a PEO offers is the lower cost of providing medical benefits for groups which are very small, say less than 10 employees and/or have someone in the team with a major medical condition which will cause rates to shoot up if the group is insured on its own in the open market. This is because, as part of the PEO, the group is insured under the master plan of the PEO where the risk is spread across a large number of employees.
This advantage turns into somewhat of a disadvantage as the employee headcount starts to grow. Let us say the company now has more than 50 employees. At this headcount, there are so many options in the open market available to the group for their health insurance needs. These may range from self-insured plans to level funded plans to fully-insured plans and many more. These options allow the employers to find a health insurance solution that best meets their employees needs. A PEO with their master plan just can not match that.
PEO Customer Service
When you are small, say around ten employees, your HR needs are limited. All you care about is that your employees get paid on time, employee taxes are filed on time, employees have benefits etc. A PEO can do all this quite well. Plus when you are small, you really can not afford to have a dedicated HR person inside the company so it works out well. When employees have issues on HR related matters, they reach out to the PEO and get their issues resolved even if it takes a little longer.
However when you start to grow, your HR needs become more complex. You start to think about the culture of the company, employee engagement, employees training and growth. You may hire people in different states. Your employees have lots of questions/issues related to benefits, PTO, payroll etc. When you or your employees reach out to the PEO to resolve some of these issues, they don’t get timely responses, sometimes they get a runaround. You soon realize that the PEO service level is not meeting your expectations and it triggers the decision to bring the HR function in-house.
PEO Fees
When you are small, you justify paying the high PEO fee, as much as $125 PEPM (Per Employee Per Month), because of savings on cost of benefits as well as savings because you don’t need inhouse HR team.
However, as mentioned above, when you reach a certain team size, let us say 50 employees, you can get a better deal on benefits in the open market plus you also need inhouse HR team to manage the complexities of a large team. With the savings in benefits gone and increased cost of hiring in-house HR team members, it is hard to justify the high cost of the PEO. In our experience, some clients have saved as much as 60% when they transitioned out of their PEO.
Things to consider when transitioning out of a PEO
If you have made the decision to leave your PEO, here are some things to consider to reduce your risk.
Best time to leave the PEO is at the end of the year
There are tax implications of leaving your PEO mid-year. Because all your taxes get reset at the start of the year, the best time to leave the PEO is at the end of the year.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Tax Implications Of Leaving Your PEO Mid-Year?
All-in-one Payroll HRIS Benefits platform
When you were with the PEO, they might have provided you access to their technology platform for all your HRIS needs. Now that you are leaving the PEO, you should look for a technology vendor like UZIO that can provide you with an all-in-one solution for payroll, HRIS, Benefits, Time Tracking etc.
Maturity of your HR team
If you are bringing the HR function in-house, it is essential that you have a strong HR team. At the minimum, you will need a strong HR generalist to manage your HR function in-house. If you are not ready to hire one, you can lean on your HRIS technology provider to provide a part time HR executive to you.
Benefits Broker
You should partner with a benefits broker that can take care of all your insurance needs from health insurance to worker comp to employers liability insurance (ELI) etc. Ideally your technology platform vendor should take care of all your insurance needs thru their internal brokers or thru their broker partners.
At any point in time if you feel like connecting with us in this respect, our team is there to help. You can use the link below to book a call with us.
Conclusion
Leaving a PEO is a major decision for the company. There is no arbitrary employee headcount number you can use to make this decision. The framework provided above should help you in making this decision.
How to choose the best timekeeping system?

Quick links
-
Introduction
-
What is a timekeeping system?
-
What are different kinds of timekeeping systems?
-
What are important features of a good timekeeping system?
-
What other systems the timekeeping system needs to integrate with?
-
Conclusion
Introduction
To pay your hourly employees, you need a timekeeping system that can accurately record the hours worked by your employees. There are many timekeeping systems in the market and as an employer, it may seem daunting to choose one. In this article we will provide you with the information you need to choose the best timekeeping system for your business.
What is a timekeeping system?
A timekeeping system, also known as timesheet system or clock-in clock-out system, allows your employees to record the hours they worked. In the past, there used to be punch-in, punch-out cards on shop floors for employees to record their time. While some employers still use that system, the nature of work has changed so much that the requirements for the timekeeping have become more complex.
What are different kinds of timekeeping systems?
The timekeeping systems vary from simple manual punch-in punch-out systems to sophisticated electronic systems.
Manual timekeeping
There are many industries where hours worked are still recorded manually. For example, in the construction industry, quite often, employees at construction sites manually record their time in the timesheets. The site supervisor collects all the timesheets and at the end of the workweek delivers these timesheets to the payroll department where the payroll administrator manually enters the timesheet data into their payroll system so that the employees can get paid. There is lots of manual data entry, these systems are prone to errors and running payroll is quite an ordeal.
Kiosks based systems
For businesses where employees come to a fixed location to perform their work e.g. a shop floor or a fixed office location, there are kiosks where employees can identify themselves and clock in and clock out their hours. Sometimes employers will use a desktop computer or an iPad which has the timekeeping system installed on it to act as a kiosk. For identification purposes, employees can enter a unique pin code provided to them or use biometrics. These systems generate timesheet data that can be either manually or electronically entered into the payroll system.
Smartphone based systems
There are lots of smartphones based timekeeping systems in the market. These systems are installed on the smartphones and are typically enabled with the “Geofence” feature. Geofence feature tracks the location of the employee at the time of clock in and clock out thus allowing the employer to control and monitor the location of time entry. The timesheet data captured on the smartphone is transferred electronically to the backend systems. These systems are used by employers who have employees on the field like contractors working at multiple locations in a day or landscaping crew moving from one location to another etc. These systems typically come integrated with a payroll system so that the data is electronically transferred into the payroll system. If not, these systems allow the employer to download timesheet data in different formats like Microsoft Excel, csv etc. which can then be uploaded into the payroll systems.
Based on the type of your business, you have the option to utilize precise project time clock app. Some of these apps are designed for remote-based workers that need to project time from their office, while there are other options designed for field workers that are actively moving from one working site to the next. For example, Workyard’s timesheet app is particularly useful for contractors and owners of construction businesses.
What are important features of a good timekeeping system?
Here is a list of features you may want to consider before selecting a timekeeping system.
Fixed location versus GPS enabled
If your business requires that your employees clock in and out from a fixed location in your office, you should look for kiosks based systems. You can use a smartphone based timekeeping system for fixed location employees but you should know that Geofencing has limitations on pinpointing the exact location so your employees might be able to clock in as soon as they enter the “geo fence” but still not reached the exact location where you want them to be.
If you have a workforce deployed in the field, a geofence enabled smartphone based timekeeping system will work best for you.
Is scheduling important to you?
If your business requires shift management or scheduling of your workforce which varies on a frequent basis, you should make sure your timekeeping system also supports shift management or scheduling functionality. This is very typical of systems used in retail stores, restaurants etc.
Integration with other systems
If your business requires your staff to use a unique system like an EHR (Electronic Health Records) solution in case of clinicians working for a mental health service provider, you may need a timekeeping system that easily integrates with the EHR system.
Does your system need to be DCAA compliant?
Federal contractors who work for DoD (Department of Defense) or other government agencies are required to use a timekeeping system which is DCAA (Defense Contract Audit Agency) compliant. DCAA performs frequent audits and contractors who are not compliant might incur penalties and in some cases termination of contracts.
Do you want to track mileage as well as time?
If your employees/contractors work in the field, moving from one job to another, you may need a system which has a Geofencing feature as well as mileage tracking feature so you can accurately track time as well as distance traveled of your crew.
What other systems the timekeeping system needs to integrate with?
The most important system the timekeeping system needs to integrate with is the payroll system because the hours worked data is used to pay the hourly employees. Many payroll system vendors like UZIO offer an integrated timesheet system. If your timekeeping system is not part of your payroll solution, you should look for a system that easily integrates with the payroll solution you are using. In the worst case scenario, where there is no integration, you will have to manually enter the timesheet data into the payroll system.
In some cases, employers may also need their timekeeping data to be integrated with their accounting system.
Conclusion
There is no dearth of timekeeping systems in the market. You should choose one that meets your unique business needs and easily integrates with your payroll system.
What is California’s FAST Recovery Act? How does it impact the Fast Food Industry?

Quick links
-
Introduction
-
Details of FAST Recovery Act
-
Impact on the fast food Industry
-
Impact on the fast food workers
-
What should you do as a fast food restaurant Owner?
-
What May Happen Next?
Introduction
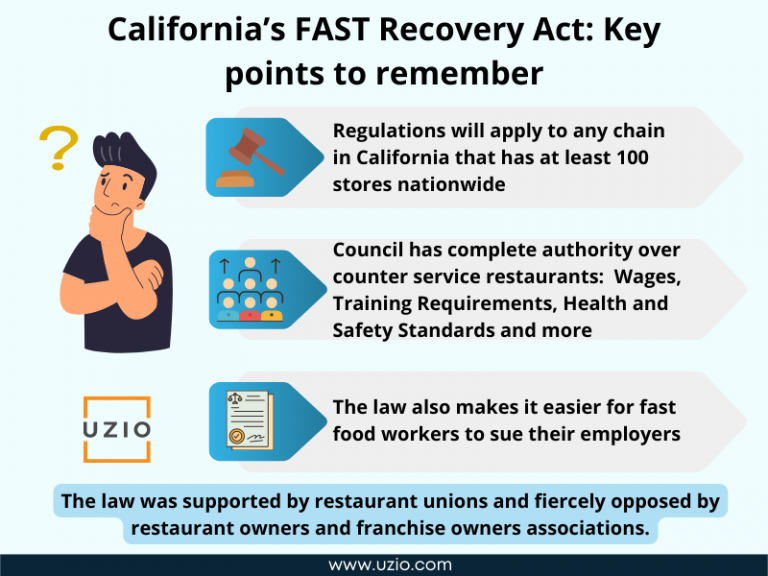
On Labor Day, California Governor Gavin Newsom signed into law the FAST Recovery Act (or AB 257). The law is aimed at the fast food industry. The law aims to enact sector wide workplace rules and standards for wages, working hours and other working conditions related to the health, safety and welfare of fast food restaurant workers. The law would establish a Fast Food Council with vast amounts of powers to regulate the wages, working conditions etc for the fast food industry in California. The law was supported by restaurant unions and fiercely opposed by restaurant owners and franchise owners associations.
Details of FAST Recovery Act
The law is aimed at fast food restaurants which are part of a fast food chain consisting of 100 or more establishments nationally (think McDonalds, Burger King and the like).
The law would establish a 10 member Fast Food Council with the power to regulate wages and set minimum standards on working hours and other conditions for fast food workers. The council has vast powers which can not be reigned in even by the legislatures. For example, the council could increase wages for California’s estimated half-million fast food workers to as much as $22 an hour starting in 2023. Currently California’s minimum wage is $15 an hour.
The law also makes it easier for fast food workers to sue their employers. According to the law, an employer would be assumed to be discriminating against an employee (rebuttable presumption which is opposite of assumed innocent unless proven guilty) if the employer discharges or takes any adverse action against an employee within 90 days of that employee making a complaint about the employer with the authorities.
Impact on the fast food Industry
The impact on the Fast Food industry in California could be far reaching. The restaurants will almost certainly be forced to raise prices to the extent they can cover higher labor costs. Typically the fast food restaurants operate on thin margins so potentially some of them may close. The restaurants might also look to technology like self-order kiosks to replace the workers. According to the restaurant owners, this law may hurt the restaurant workers it is designed to help. Other businesses who compete with the restaurants for workers might also be forced to increase wages and pass that increased cost to their customers.
Impact on the fast food workers
The law was championed by fast food workers unions. The unions have heralded the law as one of the most significant pieces of labor legislation in a generation. According to the proponents of the law, the fast food sector has been rife with abuse, low pay, wage theft, unhealthy working conditions etc. According to them, the workers routinely face serious and unacceptable risks to their health and safety which this law is supposed to fix.
What should you do as a fast food restaurant Owner?
At the minimum, you should conduct an immediate review of your employment handbooks, training, working conditions, shift schedules etc to ensure you are in compliance with the current laws of California. You may want to engage with an employment law firm to perform a complete audit of your workplace.
What May Happen Next?
There will certainly be legal challenges to the law. There is also a push by industry advocates to start a referendum effort to put it in front of the California voters for the November 2024 ballot. It is hard to say whether any of these efforts will succeed so the employers should take steps outlined above to ensure they are in compliance with the law.
What is ERC and how can I claim It?

Quick links
Introduction
At the start of the Coronavirus Pandemic, the US government passed a number of laws to help the businesses who were struggling to keep employees on the payroll. The Employee Retention Credit (ERC) program was part of one such law CARES act. It provided tax credit to businesses if they were impacted by Coronavirus shut down.
What is ERC
ERC is a refundable employment tax credit which businesses can get to help with the cost of keeping staff employed during Coronavirus shutdown. The ERC was created as part of the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act (CARES Act) in March 2020. Since then ERC has been amended twice, once as part of the American Rescue Plan of 2021 and then as part of the Infrastructure bill signed into law by President Biden in November 2021.
What Wage Period ERC is applicable to
For most businesses, ERC is applicable for wages paid between March 2020 and September 2021.
The ERC was repealed effective October 1, 2021 for most businesses by the Infrastructure bill. The sole exception was “Recovery Startup Businesses” who can claim ERC thru December 31st 2021.
A Recovery Startup Business is one that:
- Began operations on or after Feb. 15, 2020
- Maintains average annual gross receipts that do not exceed $1 million
- Employs one or more employees (other than 50% owners)
How Much Tax Credit Can I receive as part of ERC
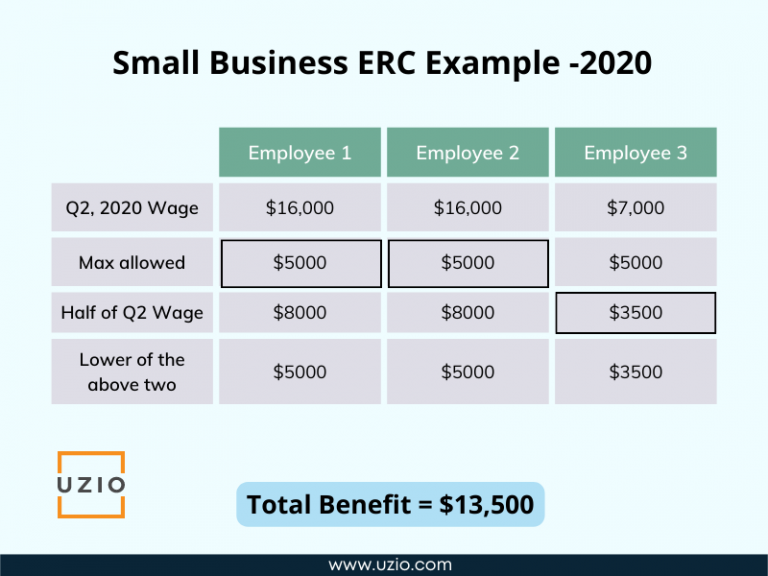
You can receive up to $5,000 per employee for 2020 and up to $7,000 per employee per quarter in 2021.
Am I Qualified to Receive ERC?
Whether you qualify as an eligible employer depends on the period. Here are the dates and the eligibility requirements.
March 13, 2020, through Dec. 31, 2020
For the period from March 13, 2020, through Dec. 31, 2020, you must have carried on a trade or business, or you must have been a tax-exempt organization that:
- Was partially or fully suspended due to COVID-19 orders from an appropriate governmental authority
- Experienced a significant decline in gross receipts, defined as less than 50% of gross receipts for the same calendar quarter in 2019
If you were self-employed, you were not eligible for the 2020 ERC for your wages.
Jan. 1, 2021, through Sept. 30, 2021
For the period from Jan. 1, 2021, through Sept. 30, 2021, you must have carried on a trade or business or were a tax-exempt organization that:
- Was partially or fully suspended due to COVID-19 orders from an appropriate governmental authority
- Experienced a significant decline in gross receipts, defined as less than 80% of gross receipts for the same calendar quarter in 2019
For this period, If you were not in business in 2019, you could use 2020 as your comparison year.
Self-employed people were not eligible for the 2021 ERC for their wages.
What Wages Will be Qualified for ERC?
What wages will be qualified also depends on the period. Here are the dates and the eligibility requirements.
March 13, 2020, through Dec. 31, 2020
If you had 100 or fewer FTE (Full Time Employees) in 2019, wages paid to all employees (providing service and not providing service) are eligible for ERC.
If you had greater than 100 FTE, wages paid to employees not providing services are qualified.
Jan. 1, 2021, through Sept. 30, 2021
For calendar quarters in 2021, if you had 500 or fewer FTEs in 201, wages paid to all (providing service and not providing service) are eligible for ERC.
If you had greater than 500 FTEs, wages paid to employees not providing services are qualified.
If I took a PPP loan, can I still claim ERC?
Yes. The ERC is available to PPP borrowers. However, the employer can not double dip meaning they can only claim the ERC on any qualified wages that are not counted as payroll costs in obtaining PPP loan forgiveness.
How Can I Claim ERC?
Employers should consult with their legal and tax advisors to whether they are eligible for ERC and how to claim it. However, here is the summary of the process to claim ERC.
Although the program was repealed for most employers by September 30, 2021, the employers can still claim the credit by filing amended payroll tax returns. Eligible businesses can file a claim for a retroactive refund on previously paid qualified wages for past calendar quarters by filing Form 941-x, Adjusted Employer’s Quarterly Federal Tax Refund.
How do you pay employees who do not have a bank account?

Quick links
-
Overview
-
Unbanked Employees
-
Pay Cards
-
What Are The Benefits of Pay Cards
-
What are Federal and State Regulations applicable to Pay Cards
-
State Regulations
-
Conclusion
Overview
Most employers pay their employees either through direct deposits in the employees bank accounts or through paper checks which are handed over to the employees or mailed to them. Lately employers have been moving away from paper checks because of the extra cost involved in printing and delivering checks to the employees. These options work great if the employees have a bank account. How do you pay employees who do not have a bank account?
In this article we will provide you with some options.
Unbanked Employees
According to a recent Forbes Article, there are close to 16 million unbanked consumers in the US. These are people who are living in households where no one has a checking or savings account in a bank. Moreover there are around 51 million US adults who are considered underbanked because they typically have poor credit ratings and are unlikely to generate meaningful income for the bank.
If you employ one of these people, how do you pay them? Let us explore different options available to you.
Pay Cards
One of the options you can use to pay unbanked employees is to use Pay Cards. Pay cards work like debit cards. Like direct deposit, payroll cards are a form of electronic payment. Each payday, the employee’s net wages are deposited directly into the pay card. The employee does not need to have a bank account to get and use the card. The Pay Cards are associated with major payment processors like Visa or Mastercard. These cards can be used at any establishment that accepts Visa or Mastercard. Plus the employee can use the card for online purchases as well as bill payments. The employee can also use the card at an ATM for cash withdrawals.
The Payroll vendors like UZIO offer Pay Cards as an added service to their employer clients (SMBs). Employees can choose to receive their pay via direct deposit, paper checks or Pay Cards. When Payroll is run, for employees who chose Pay Card as the option, the funds are instantly added to their Pay Card.
What Are The Benefits of Pay Cards
The benefits of a pay card are similar to those offered by other forms of electronic payment such as direct deposit.
Employers save on the cost of printing and depositing paper checks. The employees receive wages in a timely manner. Other benefits to employees include:
- Immediate access to wages on payday
- 24/7 access to funds through ATMs
- Ability to make in-store or online purchases
- Ability to pay bills on-line
What are Federal and State Regulations applicable to Pay Cards
Because some vendors charge high fees for use of pay cards, there are federal and sometimes state regulations that you should be aware of before implementing pay cards in your company.
At the federal level, the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) has the enforcing authority over pay cards. The CFPB prohibits employers from mandating that employees receive their wages using a pay card. The CFPB requires that the employers offer its employees a choice between a pay card and another payment method and the permissible alternative methods of wage payment are governed by state laws.
State Regulations
Below is a summary of the state laws governing the use of pay cards. You should consult the state statute for complete and specific information.
| State | Summary Regulation Governing Pay Card |
|---|---|
| Alabama | No express regulation. |
| Alaska | No express regulation. |
| Arizona | Pay cards can be offered for wage deposit if an employee has an option to receive direct deposit. Employees should be offered details of fees associated with the card and one free withdrawal for each wage deposit. |
| Arkansa | No express regulation. |
| California | No express regulation. For regulation purposes, paycards are treated similar to direct deposits. |
| Colorado | Employee should have another option to choose from and should be able to access entire wage amount free of charges each pay period |
| Connecticut | Employee should have another option to choose from and should be able to access entire wage amount free of charges each pay period |
| Delaware | Employers may issue a payroll debit card which provides the functional equivalent of cash or a check. It is the employers’ responsibility to effectuate a payroll debit card system which will allow full payment of wages on an employee’s regular payday and without cost to the employee. |
| District of Columbia | No express regulation. |
| Florida | Florida Statutes identifies payroll debit cards as a permissible method of wage payment if certain conditions are met. |
| Georgia | Employees should be able to opt-out of pay cards at any time and be paid by check or direct deposit. |
| Hawaii | Requires employee’s voluntary authorization provided certain conditions are met. Among other things, these conditions address written disclosures, alternative payment options, access to account information and cash wages without cost, fee prohibitions, and timely payment of wages to the payroll card account. |
| Idaho | No express regulation |
| Illinois | Employee should have another option to choose from and should be able to access entire wage amount free of charges each pay period |
| Indiana | No express regulation |
| Iowa | No express regulation |
| Kansas | Employers are authorized to use pay card when certain conditions are met. |
| Kentucky | Pay card authorized if the employee has access to entire wage free of any charge |
| Louisiana | No express regulation |
| Maine | Employee should have another option to choose from and should be able to access entire wage amount free of charges each pay period |
| Maryland | Pay card can be used if authorized by the employee and fees applicable to the pay card are disclosed to the employee |
| Massachusetts | No express regulation |
| Michigan | Permits the use of payroll debit cards if certain conditions are met. Among other things, these conditions relate to employee consent, access to funds in the account without cost, access to account balance information without cost, and advance notice of any changes in terms and conditions of the payroll debit card. In addition, the statute prohibits linking payroll debit cards to any form of credit and authorizes the payment of wages using direct deposit and payroll debit cards only if certain requirements are satisfied. |
| Minnesota | Permit the use of payroll cards if a variety of conditions are satisfied. Among other things, these conditions relate to ownership of the funds deposited into the payroll card account, written disclosures that must be made by employers, written consent by participating employees, and limitations on permissible fees. |
| Mississippi | No express regulation |
| Missouri | No express regulation |
| Montana | Paycards may be used if participation is voluntary and certain other conditions are met. |
| Nebraska | Paycards can be used if certain conditions are met. Requires access to full net wages at no cost |
| Nevada | Authorizes the use of electronic wage payment methods including payment on a debit card, if optional at the election of the employee and certain conditions are met. Among other things, the employee must be provided at least one free transaction each pay period, fees must be disclosed and consented to in writing by the employee, and the program may not include any restriction or requirement that a reasonable person would find to be an unreasonable burden or inconvenience. |
| New Hampshire | An employer may use payroll cards so long as employees are provided with at least one means of withdrawing the full balance from the card each pay period, at a financial institution or other location convenient to the place of employment, without any cost. Employee participation must be voluntary and may not be made a condition of hire or continued employment. Employers that offer payroll cards must comply with certain notice and disclosure requirements and must ensure that the payroll card account complies with the federal Electronic Funds Transfer Act and Federal Reserve Regulation E. |
| New Jersey | Authorizes employers to compensate their employees using payroll debit cards with the employees’ voluntary written consent and provided certain other conditions are met. Among other things, these conditions relate to employee consent, access to wages without cost or difficulty, required disclosures, and the ability to change payment methods. |
| New York | NY treats pay cards as another kind of direct deposit so all the regulations of direct deposit are applicable to pay cards. Among other things, an employee must consent in writing, it can not be a condition of employment and an employee should have full access to his/her wages without any fee. |
| North Carolina | No express regulation. |
| North Dakota | Permits the payment of wages using stored value cards issued by a federally insured bank or credit union. Among other things, the funds underlying the card must be an insured deposit and employee participation must be voluntary. |
| Ohio | No express regulation. |
| Oklahoma | Authorizes the payment of wages using “electronic means.” In this opinion letter, the state Attorney General opined that the section 165.2 must be interpreted in accordance with the federal Electronic Funds Transfer Act (EFTA) and Regulation E. Among other things, the letter addresses the circumstances under which employers may compel the payment of wages using electronic means and the electronic delivery of deduction statements. |
| Oregon | Authorizes use of pay cards and requires an agreement between the employer and the employee that meets specified conditions and addresses access to wages without cost. |
| Pennsylvania | Provides that where a law or regulation requires that a payment be made in lawful money or by check, the payment may be made by credit to an account at a financial institution, including a payroll card account, if the recipient of the payment has authorized the payment method in writing or electronically. Certain conditions must be satisfied when payroll cards are used. Among other things, these conditions relate to disclosures, cash access, fees and change in payment methods. |
| Rhode Island | Authorizes the payment of wages by credit to a payroll card account upon written or electronic request of the employee. Among other things, the statute defines “payroll card account” and requires that employees be able to make at least one withdrawal from the payroll card account each pay period without charge. |
| South Carolina | No express regulation. |
| South Dakota | No express regulation. |
| Tennessee | Authorizes the payment of wages using a prepaid debit card provided certain conditions are met. Among other things, these conditions require that employees also be given the option of being paid by direct deposit, receive written disclosure of applicable fees, and be able to make at least one withdrawal or transfer each pay period without cost for any amount contained on the card. |
| Texas | No express regulations. Wages can be paid using paycards if certain conditions are met. Among other things, the payment method must be approved by the employee in writing. |
| Utah | Authorizes the use of pay cards provided certain conditions are met. Among other things, the Rule addresses the ability to withdraw full wages on payday without cost and the conditions under which the required statement of deductions may be provided electronically. |
| Vermont | Authorize the payment of wages by credit to a payroll card account with the written consent of the employee and provided a variety of conditions are met. Among other things, these conditions relate to written disclosures, access to account information and cash wages without cost, prohibited fees, linkage to credit, and post-employment responsibilities. |
| Virginia | Permits the payment of wages using a prepaid debit card provided certain conditions are met. Among other things, these conditions relate to employee consent and required disclosures. The statute also identifies the circumstances under which paycards may be the default method of wage payment for employees hired after January 1, 2010 who do not designate an account for direct deposit. |
| Washington | No express regulations. Wages can be paid using paycards if certain conditions are met. Among other things, certain requirements must be met if there are fees for using the card. |
| West Virginia | Permits payment by deposit or electronic transfer of immediately available funds into an employee’s payroll card account in a federally insured depository institution. The employee and employer must agree in writing to payment using a payroll card. |
| Wisconsin | No express regulation. |
| Wyoming | No express regulation. |
Conclusion
For unbanked employees, a pay card is a great option to electronically receive their wages in a timely fashion. It is a safe and cost effective way to receive the wages if the employee can not avail of the direct deposit or paper check option. For employers, Pay Cards save cost and time as the wages are electronically deposited in the employees pay card without the need of printing and mailing paper checks. The employers have the legal obligation to ensure they are in compliance with federal and state regulations when rolling out Pay cards. The main regulation they need to follow is that it should be a voluntary process for employees to sign up, employees should have other options to receive wages and they should be able to withdraw their wages without incurring any cost.
Fall SMB Growth Opportunities: are you ready for it?

Overview
Fall is upon us, and with it comes a renewed sense of energy and drive. For many, it’s considered a time for renewed efforts to close business. Let’s finish the year strong. Many business owners find themselves invigorated after a hopefully relaxing summer vacation, and now’s the time to bump our growth efforts into high gear. More than 1/3rd of SMBs report that Q4 is the most profitable time of year for their business. Revenue growth numbers broken out by industry shows the following:
- Online Retailers – 74%
- Brick & Mortar Retailers – 71%
- Restaurants, bars, and caterers – 47%
- Transportation – 38%
- Real estate and property management – 33%
- IT and Software – 27%
Along with supporting this drive to grow the sales numbers frequently comes the requirement for additional resources to help support that incoming business. It’s an all-hands-on-deck time for businesses. As you gear up for this finish push to finish the year strong, This is a great opportunity to reassess how well your resources will be in terms of supporting (versus hindering) your growth. Is your payroll provider slowing you down? Are you stuck with time-consuming manual efforts and encountering payroll errors? This is a good time to look at ways to optimize these payroll processes and take advantage of tools that automate these manual processes. If you encounter issues, how well does your payroll provider make timely, live customer service available to you? Do you have a dedicated account manager there to answer your questions? While many companies have been scaling back their support services, this is not the time to cut back, rather, this is the time to provide optimal services.
As you take the time to look at how well your payroll provider supports your business, key features you should be receiving include:
- Simple setup and onboarding process
- Accurate tax filing and deposits
- Direct Deposits
- Robust Reporting
- Integration
- Employee Self Service – including a mobile app
- Top-notch customer support
If you are not getting these features, get in touch with us for an expert-led demo to learn about UZIO payroll services.
What is the EEO-1 Report? How Do I Create one?

Quick links
-
Overview
-
What is the EEO-1 report?
-
Who must file?
-
When to file?
-
How to file?
-
What data should you capture to create the report?
-
How Should I Capture this Data?
Overview
There are federal laws that make it illegal to discriminate against a job applicant or an employee because of persons race, color, religion, sex (including pregnancy, transgender status, and sexual orientation), national origin, age (40 or older), disability or genetic information.
The US Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC), the federal agency tasked with enforcing these laws, collects workforce data from employers using EEO-1 Report.
What is the EEO-1 report?
The EEO-1 report is a mandatory annual data collection report that is required to be filed with the EEOC by all private sector employers with 100 or more employees, and federal contractors with 50 or more employees. It is required by law; it is not voluntary.
Earlier the report used to consist of two components:
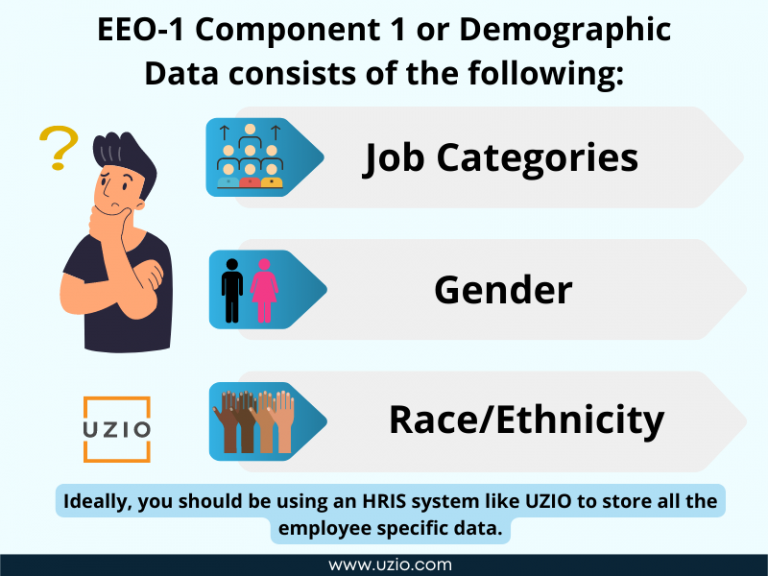
- EEO-1 Component 1 or demographic data consists of the demographic information of the employees including data by race/ethnicity, sex and job categories.
- EEO-1 Component 2 or pay data consists of aggregated wage and hours worked data by race/ethnicity and sex.
Please note that EEOC no longer requires employers to submit EEO-1 Component 2 report. For 2022 and beyond, eligible employers are only required to submit EEO-1 Component 1 data.
Who must file?
EEO-1 Component 1 report must be filed by:
- All Private employers with 100 or more employees
- All federal contractors with 50 or more employees
When to file?
The report is filed once a year. According to EEOC, the 2022 EEO-1 Component 1 data collection is tentatively scheduled to begin in April 2023. The final opening date will be posted on the EEOC website for EEO-1
How to file?
The EEOC requires that EEO-1 Component 1 Reports be submitted electronically via the EEO-1 Component 1 Online Filing System (OFS), accessible here.
There are different types of filing the employer has to do, based on whether the employer is a single-establishment employer or a multi-establishment employer.
SINGLE-ESTABLISHMENT EMPLOYERS
A single-establishment employer (i.e., an employer conducting business at only one establishment) is required to submit only one EEO-1 Component 1 Report called Type 1 Single-Establishment Report (Type 1 Report). The Type 1 Report must include demographic data for all the employer’s employees categorized by race/ethnicity, sex, and job category.
MULTI-ESTABLISHMENT EMPLOYERS
A multi-establishment employer (i.e., an employer conducting business at more than one establishment) is required to submit all the following types of reports:
Type 2 Consolidated Report (Type 2 Report):
All multi-establishment employers must submit a Type 2 Consolidated Report. The Type 2 Report must include demographic data for all employees of the employer (i.e., all employees at headquarters as well as all establishments) categorized by race/ethnicity, sex, and job category. In other words, the total number of employees indicated on the Type 3 Headquarters Report, PLUS the applicable establishment reports (i.e., Type 4 Establishment and/or Type 8 Establishment Reports) MUST equal the total number of employees shown on the Type 2 Consolidated Report.
Type 3 Headquarters Report (Type 3 Report):
All multi-establishment employers must submit a Type 3 Headquarters Report. The Type 3 Headquarters Report must include demographic data for all employees working at the main office site (i.e., headquarters) of the employer, as well as any remote employees who report to the employer’s headquarters categorized by race/ethnicity, sex, and job category. A Type 3 Report must be submitted even if there are fewer than 50 employees working at and/or reporting to the headquarters location.
Type 4 Establishment Report (Type 4 Report):
All multi-establishment employers with establishments with 50 or more employees must submit a Type 4 Establishment Report(s). The Type 4 Report must include employee demographic data for each establishment categorized by race/ethnicity, sex, and job category.
Type 8 Establishment
Report (Type 8 Report):
All multi-establishment employers with establishments with fewer than 50 employees must submit a Type 8 Establishment Report(s). The Type 8 Report must include employee demographic data for each establishment categorized by race/ethnicity, sex, and job category.
What data should you capture to create the report?
You should capture the following information for each employee to be able to generate this report:
Job Categories: Each of your employees should be placed in one of the following categories:
- Executives/Senior Level Officials and Managers
- First/Mid-Level Officials and Managers
- Professionals
- Technicians
- Sales Workers
- Administrative
- Support Workers
- Craft Workers
- Operatives
- Laborers and
- Helpers
- Service Workers
Sex
- Male
- Female
Race/Ethnicity
- Hispanic/Latino
- Non/Hispanic or Latino
- White
- Black or African
- American
- Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander
- Asian
- Native American or Alaska Native
- Two or more races
How should I capture this Data?
Ideally, you should be using a HRIS system like UZIO to store all the employee specific data. UZIO system has a built-in EEO-1 Report. If you are not using a HRIS system, you can run an employee survey to capture the required information and then manually generate the report.
QSEHRA: Best choice for SMBs to offer Cost-Effective employee health insurance

Quick links
-
Introduction
-
What is a QSEHRA?
-
How can employers offer QSEHRA?
-
Why QSEHRA could be the best choice for SMBs?
-
Conclusion
Introduction
After payroll, the health insurance premium for the employees is the largest cost for many SMBs. To be able to attract and retain top talent, SMBs have to offer health insurance coverage. So they are always looking for cost effective ways of providing health insurance coverage. Most SMBs work with their brokers to evaluate various group health plans. We think QSEHRA which stands for Qualified Small Employer Health Reimbursement Arrangement could be a great option.
In this article we will explain what is QSEHRA and why should SMBs consider QSEHRA as an option to provide health insurance coverage to their employees
What is a QSEHRA?
Let us start by saying what QSEHRA is not. QSEHRA is not a group health plan. A QSEHRA is an arrangement through which an eligible employer reimburses their employees for qualified medical expenses incurred by them or their dependents as defined by law.
It is only available for employers with fewer than 50 full-time employees. To be eligible, the employer must not offer a group health plan or flexible spending arrangement (FSA) to any of its employees and provide the arrangement on the same terms to all full-time employees meaning the reimbursement amount may only vary based on age and the number of individuals covered.
How can employers offer QSEHRA?
To offer QSEHRA to its employees, an employer should take following steps:
- Set the QSEHRA contribution amount
- This is the first step. The employers should decide how much they want to contribute towards their employees health care cost, up to an annual maximum that is set by the IRS.
- According the IRS, the 2022 QSEHRA limits for reimburse are:
- Up to $5,450 of qualified medical expenses per year (or $454.16 per month) for employee-only coverage, or
- Up to $11,050 per year (or $920.83 per month) for family coverage.
- Employers should give a written notice to their employees 90 days before the beginning of each plan year for current employees.
- Employees must purchase health insurance coverage in the individual market that provides minimum essential coverage(MEC). The employees can purchase this coverage from Obamacare Exchanges or going directly to the website of different health insurance carriers or with the help of brokers.
- Employees provide proof of coverage to their employers. After that employees can submit the receipts of qualified medical expenses which includes the premium for the health insurance coverage they purchased in the individual market, to their employers for reimbursements. The employer will reimburse the employee in tax-free dollars, for the expenses incurred up to the contribution amount set as per the IRS limit.
Why QSEHRA could be the best choice for SMBs?
- Group health plans could be expensive for very small employers
- If you are a very small employer, let us say less than 10 employees, it is very expensive to buy a group health plan. You are much better off setting up a QSEHRA where employees purchase the coverage in the individual market and you reimburse the cost of the premium and other eligible medical expenses
- Group health plans limit choice
- Employees’ healthcare needs vary a lot. Some are healthy and rarely visit the doctors office; others may have needs for very expensive medical surgery. In the group coverage, you are invariably limiting the choice by asking your employees to pick from a few options that you have chosen for the company. In a QSEHRA, you are giving your employees the option to purchase the health insurance coverage that best meets their individual needs.
- Money stays with the employer until an employee makes a claim
- Unlike group health plans, where the employer has to pay the premium to the carrier every month irrespective of whether its employees are using the healthcare system, in case of QSEHRA, the employer pays (reimburses) to the employee only when a qualified claim is submitted by the employee. Otherwise the funds stay with the employer.
Recommended Reading: As a small employer, what are your options to offer cost effective health insurance coverage to your employees?
At any point in time if you feel like connecting with us in this respect, our team is there to help. You can use the link below to book a call with us.
Conclusion
For small businesses looking to offer cost-effective health insurance to their employees, a QSEHRA could be a great option. Not only does it allow employees to choose the coverage that best suits their needs, but it also gives them tax-free money to help cover the costs. Plus, there’s no need to worry about health insurance premiums increasing; with a QSEHRA, you set your own budget each year.