List of 2023 Federal Holidays for Small Businesses That You Need To Know

Quick links
-
New Year’s Day
-
Martin Luther King Jr.’s Birthday
-
Washington’s Birthday (Presidents’ Day)
-
Memorial Day
-
Juneteenth
-
Independence Day (4th of July)
-
Labor Day
-
Columbus Day
-
Veterans Day
-
Thanksgiving Day
-
Christmas Day
There are two types of federal holidays in the United States.
First, there are paid holidays that are required by law to be observed by all private and government employers—these include holidays such as Labor Day and Veteran’s Day that commemorate events of national importance.
Then there are those holidays that are simply days off—holidays such as New Year’s Day and Independence Day that celebrate significant events in American history—which might or might not be observed depending on the individual employer’s practices.
Here’s a full list of federal holidays in 2023 so you can plan your year accordingly!

New Year’s Day
Sunday, January 1, 2023 – New Year’s Day | Monday, January 2 (observed)
Beginning on January 1, 2023 New Year’s Day will be a federal holiday honoring new years. For most Federal employees, Monday, January 2, will be treated as a holiday for pay and leave purposes.
Checkout the list of federal holidays in 2024!
Martin Luther King Jr.’s Birthday
Third Monday in January | Monday, January 16
One of America’s biggest holiday celebrations, Martin Luther King Jr.’s Birthday, is held on January 16 in 2023. On that day, thousands of communities across America host a variety of events to commemorate Dr. King’s life and work.
Washington’s Birthday (Presidents’ Day)
Third Monday in February | Monday, February 20
President’s Day is a federal holiday observed on Monday, February 20, to honor presidents of the United States.
Memorial Day
Last Monday in May | Monday, May 29
This federal holiday honors those who have died serving in the U.S. Armed Forces and takes place on May 29 this year.
Juneteenth
Third Saturday in June | Monday, June 19
Juneteenth (short for “June Nineteenth”) is usually celebrated on the third Saturday in June and commemorates the end of slavery, is a federal holiday in the United States.
Independence Day (4th of July)
Tuesday, July 4
Independence Day is a federal holiday in the US. Independence Day, or more commonly known as the Fourth of July, is a federal holiday to commemorate the adoption of the Declaration of Independence on 4 July 1776, declaring independence from the Kingdom of Great Britain.
Labor Day
First Monday in September | Monday, September 4
This holiday is held to honor American workers for their contributions to society through labor unions, minimum wage laws, and other benefits.
Columbus Day
Second Monday in October | Monday, October 9
This federal holiday is observed on October 9 this year and honors Christopher Columbus, who was born on October 12, 1451. (also observed as Indigenous Peoples Day)
Veterans Day
Friday, November 10 (observed) | Saturday, November 11
Veterans Day is an annual holiday in America honoring the 24.9 million military veterans in the United States. Veterans Day is both a federal and state holiday and is usually observed on November 11 each year.
Recommended reading: Looking for ACA Health Insurance Coverage? Learn here what is new in 2023!
Thanksgiving Day
Fourth Thursday in November | Thursday, November 23
Thanksgiving, or Thanksgiving Day as it is called by many is celebrated on the fourth Thursday in November each year.
Christmas Day
Monday, December 25 – Christmas Day
Christmas Day is celebrated in the USA on the 25th December each year. Christmas is a time of getting together with family and friends and the giving and receiving of gifts.
Does your state celebrate other holidays?
Certain U.S. states have their own state-wide holidays that are observed by state governments and banks. Some of these include:
- Nevada’s Nevada Day – the last Friday in October of every year
- Georgia’s Founding Day – a holiday that celebrates its founding on February 12, 1733
- Wisconsin has several – Casimir Pulaski Day on March 4, and Robert La Follette Sr. Day on June 14
- Hawaii Native Royalty – March 26 and June 11
Get in touch with us for an expert-led demo to know more about UZIO, the best payroll management system for SMBs.
List of 2022 Holidays for Small Businesses That You Need To Know

Quick links
-
New Year’s Day
-
Martin Luther King Jr.’s Birthday
-
Washington’s Birthday (Presidents’ Day)
-
Memorial Day
-
Juneteenth
-
Independence Day (4th of July)
-
Labor Day
-
Columbus Day
-
Veterans Day
-
Thanksgiving Day
-
Christmas Day
There are two types of federal holidays in the United States.
First, there are paid holidays that are required by law to be observed by all private and government employers—these include holidays such as Labor Day and Veteran’s Day that commemorate events of national importance.
Then there are those holidays that are simply days off—holidays such as New Year’s Day and Independence Day that celebrate significant events in American history—which might or might not be observed depending on the individual employer’s practices.
Here’s a full list of federal holidays in 2022 so you can plan your year accordingly!

New Year’s Day
Friday, December 31, 2021 – New Year’s Day (observed) | Saturday, January 1. Beginning on January 1, 2022 New Year’s Day will be a federal holiday honoring new years.
Checkout the list of federal holidays in 2023!
Martin Luther King Jr.’s Birthday
Third Monday in January | Monday, January 17. One of America’s biggest holiday celebrations, Martin Luther King Jr.’s Birthday, is held on January 17 this year. On that day, thousands of communities across America host a variety of events to commemorate Dr. King’s life and work.
Washington’s Birthday (Presidents’ Day)
Third Monday in February | Monday, February 21. President’s Day is a federal holiday observed on Monday, February 21, to honor presidents of the United States.
Memorial Day
Last Monday in May | Monday, May 30. This federal holiday honors those who have died serving in the U.S. Armed Forces and takes place on May 30 this year.
Juneteenth
Third Saturday in June | Saturday, June 19. Monday, June 20 – Juneteenth (observed). Juneteenth (short for “June Nineteenth”) is usually celebrated on the third Saturday in June and commemorates the end of slavery, is a federal holiday in the United States.
Independence Day (4th of July)
Monday, July 4. Independence Day is a federal holiday in the US. Independence Day, or more commonly known as the Fourth of July, is a federal holiday to commemorate the adoption of the Declaration of Independence on 4 July 1776, declaring independence from the Kingdom of Great Britain.
Labor Day
First Monday in September | Monday, September 5. This holiday is held to honor American workers for their contributions to society through labor unions, minimum wage laws, and other benefits.
Columbus Day
Second Monday in October | Monday, October 10. This federal holiday is observed on October 10 this year and honors Christopher Columbus, who was born on October 12, 1451. (also observed as Indigenous Peoples Day)
Veterans Day
Friday, November 11. Veterans Day is an annual holiday in America honoring the 24.9 million military veterans in the United States. Veterans Day is both a federal and state holiday and is usually observed on November 11 each year.
Thanksgiving Day
Fourth Thursday in November | Thursday, November 24. Thanksgiving, or Thanksgiving Day as it is called by many is celebrated on the fourth Thursday in November each year.
Christmas Day
Sunday, December 25 | Monday, December 26 – Christmas Day (observed). Christmas Day is celebrated in the USA on the 25th December each year. Christmas is a time of getting together with family and friends and the giving and receiving of gifts.
Does your state celebrate other holidays?
Certain U.S. states have their own state-wide holidays that are observed by state governments and banks. Some of these include:
- Nevada’s Nevada Day – the last Friday in October of every year
- Georgia’s Founding Day – a holiday that celebrates its founding on February 12, 1733
- Wisconsin has several – Casimir Pulaski Day on March 4, and Robert La Follette Sr. Day on June 14
- Hawaii Native Royalty – March 26 and June 11
Get in touch with us for an expert-led demo to know more about UZIO, the best payroll management system for SMBs.
Payroll Company Implementing COVID-19 Supplemental Paid Sick Leave Law (SB 114)

Quick links
-
Introduction
-
SB 114 Implementation: Effective Date; Covered Employers
-
Who qualifies for SB 114?
-
What are the Employee’s Rights?
-
What are the Employer’s Rights?
-
Miscellaneous Rules
-
How to avail SB 114?
-
What Employers Need to Know About SB 114 and how it is going to affect them?
-
How Payroll Company Implement SB 114 in California
-
Notice Requirements
-
Conclusion
On February 9, 2022, Governor Gavin Newsom signed SB 114, effective February 19, 2022. The law requires covered employers to provide up to 80 hours of COVID-19 Supplemental Paid Sick Leave (“SPSL”) to covered employees who are unable to work or telework due to certain reasons related to COVID-19. with up to 40 of those hours available only when an employee or family member tests positive for COVID-19.
SB 114 is similar, but not identical, to California’s previous SPSL law, which expired in September 2021. The key provisions of SB 114 are summarized below.

SB 114 Implementation: Effective Date; Covered Employers
SB 114 became effective on February 19, 2022. However, employees can retroactively request SPSL to cover eligible absences going back to January 1, 2022.
- SB 114 applies to employers with 26 or more employees
- Covers COVID-19 sick leave from 1/1/2022 to 9/30/2022
- For an employee who needs a diagnosis of COVID-19, or needs to quarantine or isolate
For an employee who needs to care for:
- a family member who is quarantining or isolating, or
- for a child whose school or child care is closed because of COVID-19 on the premises
Can be used to take time to get or recover from the vaccines.
Who qualifies for SB 114?
You qualify for California’s permanent paid sick leave law if you worked:
- At least 30 days in California in a year
- After 90 days on the job
- Full-time, part-time or as a temporary worker
Most workers are entitled to permanent paid sick leave, earning one hour of paid leave for every 30 hours worked. The sick leave that employers are required to provide may be capped at 24 hours or three days per year.
Cities or regions in California may require employers to provide additional sick leave. For example, the City of Los Angeles requires a minimum of six paid sick leave days per year.
What are the Employee’s Rights?
- Employees can take up to 40 hours of COVID-19 supplemental paid sick leave but shall not exceed 80 hours for the period between January 1, 2022 and September 30, 2022.
- Test positive for COVID-19 more than 40 hours: Employees can take up to 40 more hours if tests come back positive for COVID-19. Employees do not have to use the first 40 hours to qualify for the extra 40 hours granted.
What are the Employer’s Rights?
- An employer may limit it to 3 days or 24 hours unless the employee provides verification from a health care provider.
- If that employee tests positive, Employer is authorized to require the employee to submit to another test on or after the fifth day, after the first positive test and provide documentation of those results.
- No obligation to provide additional COVID-19 supplemental paid sick leave if the employee refuses to provide documentation of a test result.
- An employer shall not be required to pay more than five hundred eleven dollars ($511) per day and five thousand one hundred ten dollars ($5,110) in the aggregate to a covered employee.
Miscellaneous Rules
- Employers cannot require employees to first exhaust their SPSL before satisfying any requirement to provide paid sick leave related to COVID-19 under any CAL-OSHA COVID-19 Emergency Temporary Standard.
- If an employee has already received paid time off for a COVID-19-qualified reason, since January 1, 2022 and before February 19, the employee is entitled to be credited back any paid time off, vacation time or other paid sick leave that the employee received. Similarly, if the employee did not receive paid sick leave for work time missed because of a qualified reason between January 1 and February 19, the employee will be entitled to receive such SPSL now.
- Unlike last year’s legislation, no provision allows for employers to apply for tax credits for SPSL payments made to employees.
How to avail SB 114?
Tell your employer as soon as possible that you will need to use your paid sick leave hours or ask about other leave benefits.
If you were not paid for the sick leave you took previously, you can still file a wage claim.
- Keep track of your hours and pay stubs
- Document communication with employer
- Contact the Labor Commissioner’s Office near you
SB 114 Supplemental Paid Sick Leave Request Fillable Form link is here.
What Employers Need to Know About SB 114 and how it is going to affect them?
SPSL leaves taken must be reported as SPSL hours used on each pay stub. Beginning the next full pay period following February 19, 2022, SPSL and other sick leave used must be displayed separately on employee pay stubs, and retroactive payments must be displayed on pay stubs for the period during which payments are made. If no SPSL was used during the payroll period, then the pay stubs should display zero hours.
Employers should verify with their payroll departments, or with outside payroll vendors, that these new pay stub requirements are known and will be followed.
How Payroll Company Implement SB 114 in California
To make sure their customers in California are in compliance with SB 114, the payroll vendors need to change their systems. The most important change is related to the information that is displayed on the pay stubs.
Normally the employee pay stub will show the time off “Accrued in Current Period” and the “Balance” as shown below.
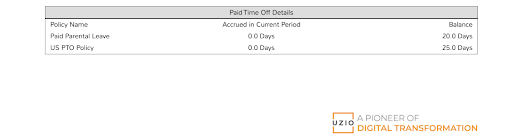
Going forward, to accommodate for the requirements of SB 114, the pay stub should also display SPSL used. If no SPSL was used during the payroll period, then the pay stubs should display zero hours. Here is a sample of what PTO detail section of the pay stub should look like to be in compliance with SB 114:
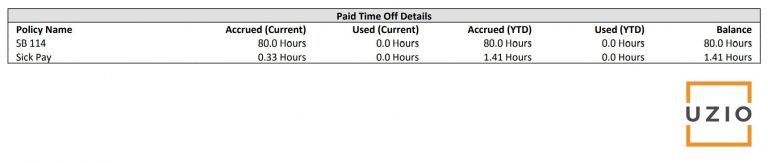
Recommended Reading: Biggest pain point with Payroll and HR software
At any point in time if you feel like connecting with us in this respect, our team is there to help. You can use the link below to book a call with us.
Notice Requirements
Employers must post in a conspicuous location in the workplace, and disseminate by electronic means to employees who do not frequent the workplace, the new SPSL requirements and rights. The Department of Industrial Relations (Labor Commissioner) is required to make a model poster publicly available by February 16, 2022.
Conclusion
Employers in California are scrambling to be in compliance with SB 114. They are urging their payroll vendors to roll-out support for SB 114 at the earliest possible. Uzio has implemented the changes required to support SB 114 and rolled it out to its clients in California. If you are looking for a payroll vendor who understands SB 114 and whose systems are already in compliance with SB 114, you can reach out to us at using the link below.
How to Simplify Your Small Business Payroll Process

Quick links
-
Introduction
-
Step 1. Make sure your business is registered with the IRS
-
Step 2. Secure completed form W-4 from your employees
-
Step 3. Register in the state for state withholding and unemployment tax
-
Step 4. Make correct classification for exempt and nonexempt employees
-
Step 5. Select Correct Deduction Method
-
Step 6. Select Correct Payment Method
-
Step 7. Enter time card entry
-
Step 8. Run Payroll
-
Step 9. File your Form 940 and Form 941
-
Step 10. Make your tax deposits
So you decided to start a business! Congratulations.
Among the tons of things you will be responsible for, one will be to process payroll for your employees. While you can always use a payroll software provider like Uzio to ease your burden, if you decide to do it yourself, here we will share with you the steps you can take to simplify your small business payroll process.
In fact we have helped hundreds of companies since 2018 to successfully transition from their existing Payroll provider to Uzio.
The following tips will help you get started on simplifying your small business payroll process and getting back to running your business efficiently and profitably.
Step 1. Make sure your business is registered with the IRS
When you process the payroll, you will have to withhold federal income tax from your employees wages and deposit it with the IRS. To be able to do that, the first thing you will need is an EIN (Employer Identification Number) which is issued by the IRS.
You can apply for the EIN online by going to the official website of the United States Government.
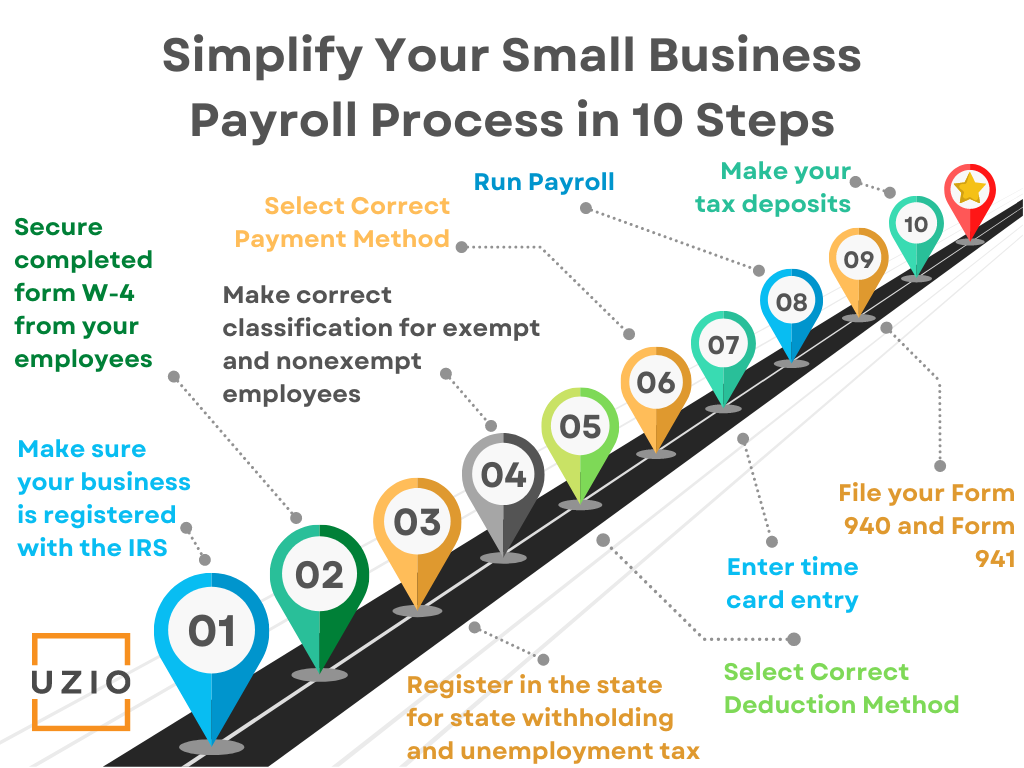
Step 2. Secure completed form W-4 from your employees
You will have to secure a completed W-4 form from your employees to know how much federal income tax to withhold from their wages. Each employee should give you his/her signed copy of the W-4 form.
Step 3. Register in the state for state withholding and unemployment tax
You will also have to register your business in your state to be able to withhold state taxes from your employee wages as well as pay for state unemployment tax.
Every state does it their own way so your best option is to go to the state’s small business website to find out these details.
Please note that if you have hired employees in states other than where your business is incorporated, you will have to withhold wages and pay state unemployment tax in that state as well.
Step 4. Make correct classification for exempt and nonexempt employees
Before you can run payroll, you will have to make sure you correctly classify each employee as Exempt or Non-Exempt.
Employees who are classified as Exempt employees, are not entitled to overtime pay as guaranteed by the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) whereas the Non-Exempt employees are entitled to the overtime pay. The other difference between exempt employees and nonexempt employees is that exempt employees receive a salary for the work they perform, while non-exempt employees earn an hourly wage.
Step 5. Select Correct Deduction Method
A deduction from employee wages can be pre-tax or post-tax so please make sure you choose the correct deduction method. For example, if you offer medical/dental/vision coverage, the employee portion of the premium for these benefits should be deducted pre-tax from their wages. The same is true for retirement benefits like 401K etc.
Step 6. Select Correct Payment Method
Are employees getting paid via checks or ACH or a combination of both. For those employees who are getting paid via ACH, please make sure you have their correct banking information.
Step 7. Enter time card entry
If you have hourly employees who get paid based on hours worked, you will have to calculate their total hours worked for the pay period. If they did not earn overtime, total hours worked times their hourly rate would be their gross pay. If they did work overtime, you will need to compute their overtime pay based on the overtime pay rules in your state. In most cases, overtime pay rate is 1.5 times of the hourly rate.
Step 8. Run Payroll
If you have completed all the steps outlined above, you are ready to run payroll! You will have to do it for each pay period before the pay date. If you get tired of doing it manually, you can always use Uzio Payroll Software where it can be done in minutes instead of hours.
Recommended Reading: Biggest pain point with Payroll and HR software
At any point in time if you feel like connecting with us in this respect, our team is there to help. You can use the link below to book a call with us.
Step 9. File your Form 940 and Form 941
Your responsibility does not end as soon as you process the payroll. You have to file different forms with the IRS and the state agencies. Generally, employers are required to file Forms 941 quarterly. Employers are also generally required to file Form 940 annually.
Recommended reading: A Guide to Essential Payroll Forms & More for Small Business Owners
Step 10. Make your tax deposits
Monthly or semiweekly deposits may be required for taxes reported on Form 941 (or Form 944), and quarterly deposits may be required for taxes reported on Form 940. It is very important that you make these deposits timely if you want to avoid receiving penalties from the IRS.
Conclusion
While here we have given you tips to simplify your small business payroll process, you can see that it is not easy to run your payroll manually.
A small error or delay in making tax deposits can result in thousands of dollars in penalties. You might be better off working with a company like Uzio where we guarantee your payroll would be accurate and you will not get in trouble with the IRS.
What is the least disruptive way to change payroll companies

Quick links
-
Reasons to change the current Payroll provider
-
Best time of the year to switch Payroll company
-
Steps involved in switching your Payroll provider
-
Why choose Uzio?
-
Contact Uzio
Selecting a new Payroll provider for your business can seem like an overwhelming process at first. But don’t worry, we are here to help!
In fact we have helped hundreds of companies since 2018 to successfully transition from their existing Payroll provider to Uzio.
If you’re looking at changing payroll companies, be sure you understand how it will affect you before you make any decisions!
The most important thing when choosing payroll company is knowing which features are most important in order to make an informed decision on which company will best suit you needs!
This could be an article describing all possible changes in detail so you can make an informed decision on which one is best suited for you?
In this blog we are going to cover the following:
- Reasons to change the current Payroll provider
- Best time of the year to switch Payroll company
- Steps involved in switching your Payroll provider
- Why choose Uzio
Major reasons to switch Payroll company
You must have encountered at least one of the following issues that is leading you to search for a better solution. This list is based upon our interactions with clients that have moved to us.
| Area of concern | Impact Type | Potential Loss/Reason |
|---|---|---|
| IRS penalties | Financial loss | Thousands of dollars of potential loss because the payroll provider did not file your taxes on time |
| State penalties | Financial loss | Thousands of dollars of potential loss because the payroll provider did not file your taxes on time |
| Inaccurate W2s | Poor Employee Experience | Employees can not file taxes ontime |
| Lack of integration with your timecard system | Manual work | Waste of time and money, inaccurate payroll because of errors |
| Lack of integration with your GL system | Manual work | Inaccurate financial statements because of potential errors |
| Poor reporting capabilities | Poor Employee Experience | Waste of time and money |
| Poor customer service | Poor Employee Experience | Hours of time wasted to get simple answers |
| Exorbitant Cost | Financial loss | Nickel and dime for various payroll items |

Recommended Reading: Biggest pain point with Payroll and HR software
Best time of the year to switch Payroll company
- At the beginning of the year
- The beginning of a new quarter
At any point in time if you feel like connecting with us in this respect, our team is there to help. You can use the link below to book a call with us.
Steps involved in switching of your Payroll company
Once you have selected your new payroll provider, here is the breakdown of steps (or the list) which you should follow, for the least disruptive way to switch your payroll company.
- Ask your new payroll provider to give you their “client onboarding plan”. It will typically involve them sharing a checklist of items you will need to collect before your onboarding can commence
- Ask for a detail demo and training of their solution
- Setup a “kick off” meeting with your new payroll provider where they will walk you thru their onboarding process
- Collect the following information from your current payroll provider and share it with your new Payroll provider:
-
Employee census including their withholding details and their banking information if getting paid via ACH
-
Employee payroll registers for all the payrolls run in the current year
-
Copy of your 940/941 filed by your current provider
-
GL setup information including charts of accounts related to payroll expenses
-
Timecard setup information
-
Employee benefits information
-
PTO policies
-
Workers Compensation codes and rates
-
State withholding account details
-
State Unemployment Insurance details
-
Details for all the earnings, deductions and contributions
-
- Once your New Payroll provider has completed the payroll setup using the information provided, verify all the information in the new system
- Run at least two “Dummy Payrolls” in the new system and compare the results with the actual payroll run in the existing system. The numbers should match up-to the last cent. If not, your new payroll provider should be able to explain any differences to your satisfaction. For example, maybe an employee changes her withholding in the new system which will cause her pay and taxes not to match with the existing payroll.
- After doing a couple of “parallel payroll runs”, if you are convinced that the numbers coming out of the new payroll system are correct, you are ready to run your next payroll in the new system.
Why choose Uzio (over others in SMB segment)
Uzio is the one-stop Payroll, Benefits & HR Software for your business. It is the most affordable, simple & fully integrated cloud-based platform your business needs today.
So if you are looking for the most intuitive self-service portal, that provides you with a one-stop-shop for all your HR, Benefits, Payroll, and time tracking needs and also offers your employees an easy-to-use fully integrated solution.
Biggest pain point with Payroll and HR software

Quick links
-
Inaccurate Tax Calculation
-
Accurate Tax Filing
-
Costs
-
Support
-
Time Card Data Entry
-
Payroll Compliance
-
Challenges in Handling Remote Work
-
Threat To Data Security
-
Flexibility
-
Challenges In Payroll Computation
-
Overcoming The Payroll Challenges in 2022 and going forward
When you run your own business, it’s not enough to just know the ins and outs of your industry or have great vision for the future of your company.
You also need to have an in-depth understanding of all the nitty-gritty details, including payroll.
Payroll isn’t something that most small business owners spend much time thinking about, but it can turn into a complex nightmare if you don’t handle it right.
While there are no hard and fast rules when it comes to managing payroll, there are plenty of best practices that can help you run payroll smoothly.
For e.g. quick direct deposit is a must for any good payroll software. According to the “Getting Paid In America” survey 2021, 95.88% of respondents receive their pay through direct deposit. Which was 93.87% (2% less) in the 2020 survey.
In this article we are going to cover all the major issues a small business encounters with their payroll software/company and how to deal with them.
At any point in time if you feel like connecting with us in this respect, our team is there to help. You can use the link below to book a call with us.
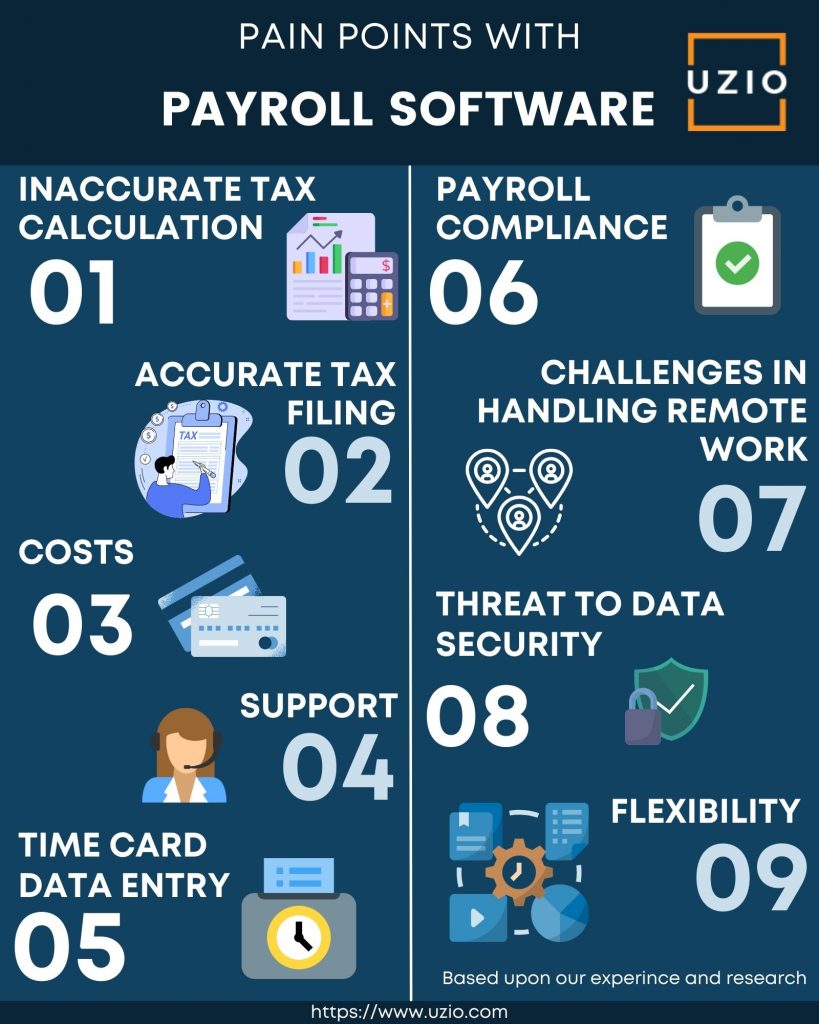
So coming back to the topic, here are key issues w.r.t your Payroll software:
1) Inaccurate Tax Calculation
The biggest pain point faced by businesses from their Payroll software is inaccurate calculation and filing of taxes. Ensuring that all tax obligations are met is no easy task because of the complexity and the ongoing changes in the state and federal income taxes laws.
The problem is compounded by the inability of the payroll software vendors to make timely changes in their software to account for the changes in the tax laws and regulations.
It is not uncommon for local jurisdictions in a state to add/modify their tax laws. There are thousands of such jurisdictions. Tracking tax law changes across these jurisdictions can be very complex and costly.
Many payroll software vendors are not able to keep pace with all these changes. That is why employers should be careful when they select their payroll vendor and make sure their vendor has a proven track record of accurate tax calculations across all 50 states.
If you are facing issues with your tax calculations, our team can help. Please use the link above to schedule a demo of our payroll software.
2) Accurate Tax Filing
Even if your payroll software is calculating taxes correctly, there can be issues with tax payments to state and federal agencies. The roots of these kinds of problems can be traced back to the lack of tested and proven client onboarding procedures used by your Payroll software vendor.
When you are switching payroll vendors or starting fresh with a new payroll system, your vendor will ask you to collect and transfer tons of information about your business.
For example, you will share what is your Federal Tax Deposit Schedule.
Is it monthly or semiweekly etc.? If this information is not accurately captured by your Payroll vendor, it may lead to missed tax payments to the IRS and may result in hefty penalties.
It is very important that your Payroll vendor has proven and tested procedures in place to accurately transfer key information about your business into their Payroll software.
If you are facing issues with your tax filings, our team can help.
3) Costs
The costs of running a payroll for a small company can quickly add up. The pricing method used by Payroll vendors varies widely. There are some vendors who use a flat fee per employee per month often referred to as PEPM plus a small base fee.
In this model, the customer is not nickeled and dimed for every other task.
There are other vendors who would offer you attractive prices to lure you away but there are tons of hidden costs and the total cost of running the payroll is enormous for the customer.
For example, these vendors will charge extra when you run multiple payroll in a month or when you ask to make changes to the prior payroll data or if you ask to print the checks etc.
When you are evaluating payroll vendors, make sure you are comparing apples to apples by taking into account all the costs and not just what is advertised upfront by the vendor. Running Payroll for your business will not be very expensive if you have done the due diligence upfront.
Learn more about UZIO Payroll Software pricing and other details.
4) Support
Not being able to get timely and accurate answers to your questions, when you are under a deadline to approve Payroll is one of the biggest pain points faced by businesses.
More often than not, there is a scramble to approve the payroll so that your employees get paid on time and many times, at the last minute, you run into an issue.
For example, one of your employees informed you that she has moved to a new state or she had a baby and she changed her medical benefit plan or her banking information has changed.
You urgently reach out to your Payroll vendor where you are on hold for hours.
When someone does come on line to answer your question, they have no knowledge of your business and you end up educating them for hours before you can get any answers.
If you have been in situations like this, you are not alone!
We hear these stories time and again from customers who have switched to Uzio’s Cloud Based Payroll Management System for their payroll because they did not receive proper and timely support from their vendor.
5) Time Card Data Entry
If you employ hourly employees, before you can process their payroll, you have to enter their hours worked into your payroll system.
If you use a time card entry system, the chances are that it is not the same as your payroll system.
This means you have to manually enter the data generated from your time card system into your payroll system. This is very time consuming and very error prone.
You should look for a payroll system that also has the time card data entry system, like we do at Uzio.
In Uzio, the time card data flows seamlessly into the payroll system so you save tons of time and have less errors running your payroll.
6) Payroll Compliance
Employers are responsible for paying all their employees properly, on time, and accurately. No exceptions.
That means withholding income taxes, matching FICA contributions, paying unemployment insurance taxes (if applicable), keeping accurate records of wages paid, hours worked, etc.
If you think about it, it’s an amazing amount of responsibility to put on someone running a small company without lots of resources or time.
That’s why there are payroll services that can take some or all of these responsibilities off your plate—so you can concentrate on what really matters: your product or service.
However, if you aren’t sure whether these services are right for you—or just want to learn more about how they work—you can contact us and we can share our expertise in the field to answer your questions.
7) Challenges in Handling Remote Work
Working remotely is an increasingly common reality for many employees these days. In fact, nearly 4 in 10 American workers currently do at least some of their work from home or via a mobile device.
And while that’s certainly good news for employers who want access to top talent, it presents new challenges in managing payroll.
Furthermore, during the pandemic, the typical onboarding and offboarding process, which involves many documentation and face-to-face meetings, was no longer feasible.
In such circumstances, a system that can automate remote attendance, leave requests, training, and other HR and payroll operations is more important than ever.
8) Threat To Data Security
Small-business owners may not have time for payroll administration, but that doesn’t mean they are not exposed to potential data breaches.
Companies with fewer than 50 employees are more likely to be hit by a data breach than companies with more than 1,000 employees.
These businesses are also much less likely to report data loss incidents—meaning it might take longer for issues like identity theft or fraud charges to show up on their accounts.
From simple things like support for “Two-Way Authentication” to more complex things like being SOC 1, SOC 2 compliant, your vendor should be able to convince you that your data is secure with them.
At Uzio, we have made data security our top priority. (Here are the details)
9) Flexibility
Payroll is one of those areas where we’d love for there to be a one-size-fits-all solution, but unfortunately, there isn’t.
Each company and employee is different, which means that every payroll system should be too.
If you’re planning on outsourcing your payroll function or switching providers at some point in your company’s life cycle (and many SMBs do), it’s important to find a provider that can adjust as needed.
More than likely you won’t want – or need – all of your options from day one; having a provider that can grow with you is key.
Challenges In Payroll Computation
With so many moving parts, it’s no wonder that even some of the smallest companies find payroll to be challenging. Making your processes better will pay dividends down the road; make sure you’re not overlooking these five common mistakes:
- Payroll errors aren’t always taken seriously as they can have a huge impact on a company’s bottom line
- The process of updating systems for each new employee is frustratingly tedious for all involved
- Keeping track of wages, taxes, employer contributions and more can be overwhelming at times
- When employees are unhappy with their salary structure, others may follow suit in an attempt to earn more
- There is always pressure when deadlines loom—but it’s important to keep things in perspective
Overcoming The Payroll Challenges in 2022 and going forward
Deloitte’s Payroll Operations Survey 2020 found that 61% of organizations currently use a cloud-based payroll solution, and the top three areas of improvement associated with their payroll software are compliance, accuracy, and self-service capabilities.
A lot of new small businesses often look for ways to save money wherever they can. Payroll software, however, is often one of those expenses that feels necessary in order to run a successful company.
The American Payroll Association 2018 report mentions that “49% of U.S. workers will leave a job after experiencing just two problems with their paychecks”. Additionally, organizations using software with both timekeeping and payroll capabilities were 44% more likely to have a low rate of payroll error.
But with so many options out there that seem too good to be true, it’s not always easy for companies—especially on a budget—to know which one is right for them.
Learn more about UZIO Payroll Software for Small Business or request for a free trial.
What Is Child Tax Credit in 2022 and how it is different from Child Tax Credit in 2021?

Quick links
-
What is a child tax credit?
-
What is the major difference between CTC 2021 and CTC 2022?
-
What is in store for CTC in 2023 and beyond?
The Child Tax Credit (CTC) helps families with qualifying children get a tax break. The CTC has changed significantly from 2021 to 2022. In this article we will explain these changes.
What is a Child Tax Credit (CTC)?
The Child Tax Credit (CTC) gives you a dollar-for-dollar reduction of your taxes for each dollar spent on raising children under 17 years.
To explain the difference between 2021 and 2022 CTC, let’s start with 2020. Back then, the CTC was $2,000 per child age 16 or younger. It was also phased-out if the modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) was more than $400,000 on a joint return and more than $200,000 on a single or head-of-household return.
In 2021, the CTC was significantly enhanced. As part of the American Rescue Plan Act of 2021, signed into law by President Biden, the CTC was increased to $3,600 per child under 6 years old and $3,000 for each child ages 6-17. In addition to the increased amount, families could elect an advance payment from July through December. This was a novel twist. The IRS paid half of the total credit amount in 2021 in advance through monthly payments issued from July to December of 2021.
In 2022, CTC has reverted back to $2,000 per qualifying child as it was in 2020. The advance payment from the IRS against the CTC was also stopped. In 2022, you qualify for the full amount of CTC for each qualifying child if your MAGI is below $200,000 for single filers and $400,000 for joint filers. After these thresholds, the credit reduces by $50 for every $1,000.
What is the major difference between CTC 2021 and CTC 2022?
The first major difference is in the amount of CTC itself. As stated above, in 2021, taxpayers with children ages 6 to 17 could get a credit of up to $3,000 and for children under 6, the amount was $3,600. Compared that to 2022 where the CTC amount has reverted back to $2,000 per child 16 years of age or younger.
The second difference is that there is no advance payment from the IRS against CTC in 2022 as there was in 2021.
The third difference is in the income phase out rules. In 2021, there were two phase out rules. The first one applied to the “extra credit” amount added specifically to the 2021 CTC over 2020 CTC. If your MAGI was more than $75,000 for a single filer and $150,000 for joint filer, the CTC was phased out by $50 for every $1,000 over those thresholds. The second phase out was the same as in 2020 which was for MAGI in excess of $200,000 for single filer and $400,000 for a joint filer.
In 2022, the phase out rules have reverted back to 2020 levels, $200,000 for single filers and $400,000 for joint filers.
What is in store for CTC in 2023 and beyond?
There is a strong push in the congress, especially by democrats, to expand CTC. Considering the current makeup of the Senate which is split 50-50, democrats will need the support of a number of republicans to get over the 60 vote hurdle in the senate to pass any changes to CTC. This means democrats will have to agree to some of the changes important to republicans like the work requirements to receive the CTC. Of course, all this can completely change depending upon the results of the midterm elections due in November (2022) this year. At this time, it is best to wait and watch for the control of the house and senate before making any predictions about the proposed changes to CTC in 2023 and beyond.
What small business owners should know about benefits management?

Quick links
-
What do you mean by benefits administration?
-
What are the different types of benefits?
-
Why should small business owners care about employee benefit plans?
-
Employer responsibility and cost management
-
Stay compliant with federal and state laws
A small business can be defined as an independent entity with less than 500 employees, and it’s estimated that there are over 32 million such businesses in the United States alone in 2021 (as per Oberlo’s report).
If you’re one of these small business owners, you know how difficult it can be to run your company on a day-to-day basis, especially when handling both your company’s finances and employee benefits.
But keeping your company’s benefits costs in line doesn’t have to be complicated or overwhelming!
The following are some quick tips to help you manage your small business’s benefits cost, effectively and efficiently.
What do you mean by benefits administration?
The overall process of determining which benefits to offer employees, managing costs associated with those benefits, and distributing that information to employees is what’s meant by benefits administration.
These processes are sometimes overseen by a dedicated employee or an outside firm. The former is referred to as a ‘family’ plan, while an outside firm is called a third-party administrator (TPA).
In either case, it’s important to know exactly what you’re getting for your money. If you don’t, then expect your benefit costs to spiral out of control faster than Linda Blair in The Exorcist. And if you’d rather not be responsible for overseeing these processes, then consider hiring someone who can do it on your behalf – be it internal or external.
What are the different types of benefits?
Common types of benefits offered by employers include basic medical, dental, vision, life insurance, health savings accounts (HSA), disability insurance, and flexible spending accounts (FSA).
Recommended reading: 10 Employment Benefits to Ensure a Happy Workplace
Some organizations offer additional items such as a company-sponsored retirement plan. These are generally handled by third parties to avoid becoming overburdened with administrative work.
For example, HSA plans are arranged through banks or credit unions. The employer chooses an administrator that offers services tailored to small businesses. Employers may receive special incentives from these institutions which can make their costs even lower than what is normally available to individuals.
There is not much difference between designing a plan for an individual employee and one for multiple employees. There will be some complexities in administering group benefits options but it shouldn’t be difficult once you know how it works. Most employees prefer their benefits to be easy to understand so make sure you explain all options clearly in your policy manual along with any pertinent rules related to enrollment or usage.
Why should small business owners care about Employee Benefit Plans?
Small businesses that don’t offer their employees benefits are missing out on significant advantages. Benefits allow employers to attract top talent, which increases productivity and leads to greater organizational success.
Employers who offer health insurance, for example, can reduce turnover, since employee-friendly benefit plans are an important reason employees stay with a company for an extended period.
Businesses also save money in several ways when they provide their workers with benefits; however, some employers still shy away from offering worker perks because they believe they aren’t financially capable of doing so.
This is especially true if your organization is just starting or doesn’t have many resources at its disposal. But, most companies can afford to fund at least one employee benefit plan—health insurance—even if they’re operating on a shoestring budget.
Employer responsibility and cost management
Employers are required to provide a variety of employee benefits, which may include health insurance, life insurance, disability insurance, long-term care insurance, retirement savings plans such as 401(k) plans, vacation time, and sick leave.
Recommended reading: 10 Employment Benefits to Ensure a Happy Workplace
Employers must make timely payments on these obligations. An employer is considered liable for any payment if it is determined that they knew or should have known about an underpayment or nonpayment. This means employers who rely upon their payroll provider to manage these costs cannot pass responsibility onto them.
If you’re looking to reduce your exposure through outsourcing, consider whether your payroll service provider can handle all aspects of benefits administration before signing on.
Stay compliant with federal and state laws
Be aware that small business owners are responsible for administering employee benefits—you can’t outsource responsibility.
In addition to ensuring your plan is compliant with federal and state laws, you also need to understand all aspects of your benefits offerings, from eligibility requirements to open enrollment. You may be responsible even if your plan isn’t self-funded.
If you do use a third-party administrator (TPA), make sure they’re familiar with ACA legislation.
ACA requires that employers offer health insurance coverage to full-time employees. However, if you’re not considered an applicable large employer (ALE), you don’t have to meet ACA requirements. Regardless, it’s still essential to be knowledgeable about all laws in your state, which can include any restrictions or additional legislation on health care coverage.
UZIO is an all-in-one solution that combines benefits management with payroll & HRIS to ensure you have one platform to manage everything.
With UZIO’s world-class benefits administration solution you have the advantage to choose from a wide range of benefits offered by registered benefits brokers or you can choose to bring your own broker.
Work with your broker to create a digital benefits package with a wide variety of product categories including medical, tax-saving, and ancillary plans.
What is Form 940 and What It Means to Small Business Owners?

Quick links
-
What is form 940?
-
Who Should File IRS Form 940?
-
When Should a Company File IRS Form 940?
-
How to file form 940 online?
-
What is the difference between form 940 and 941?
-
Can I automate the entire process?
The Federal Unemployment Tax Act (FUTA) requires that businesses pay federal unemployment tax (FUTA) if they meet certain employee compensation thresholds and have $1,500 or more in employment taxes during any calendar quarter.
Form 940 (PDF), Federal Unemployment Tax Return, is the form employers use to report their FUTA tax liability to the IRS. The amount you owe depends on how many employees your business has and the wages you paid each calendar quarter.
FUTA tax contributions come out of your taxable payroll, so they lower your net take-home pay every pay period.
What is form 940?
This form is used by employers to pay Social Security and Medicare taxes.
Both employers and employees must pay these taxes, although there are different rates for each group. Typically, an employer pays 6.2 percent of employee wages into Social Security, while paying 1.45 percent of employee wages into Medicare.
Employees also pay 6.2 percent in Social Security taxes, but they do not pay any money into Medicare.
Employers do report Social Security and Medicare taxes withheld from workers’ paychecks on form W-2; workers who earn more than $200,000 per year ($250,000 if married) must report their income separately on schedule SE.
Recommended reading: What is a W2 form and why is it important for small business owners?
The IRS provides several worksheets that use information from both forms W-2 and SE to compute your total social security tax liability on form 940.
However, some businesses or individuals may need to fill out a special version of form 940 that reports self-employment earnings.
These taxpayers don’t typically have a payroll department or monthly withholdings from worker paychecks. In many cases, they must make quarterly estimated payments directly to the government instead of having withholdings paid for them.
Who Should File IRS Form 940?
Employers in most industries must file IRS Form 940 for each quarter of their tax year.
This includes individuals who operate sole proprietorships, partnerships, S corporations, or C corporations. The main exceptions are employers with 25 or fewer employees who pay $1,500 or less in wages in a calendar quarter.
If your small business meets both criteria—the employment count and wage threshold—then you do not have to file IRS Form 940 for that period.
This means if you only hire one employee to help out around your farm during harvest season, you don’t need to file IRS Form 940.
On the other hand, if you hire five workers on an ongoing basis for gardening work throughout spring, summer, and fall—even if they are considered part-time laborers—you still need to file IRS Form 940 until either of those conditions changes.
When Should a Company File IRS Form 940?
Many situations could lead a business owner to file IRS form 940.
However, if your company had no tax liability for 2020 or 2021, it won’t be necessary for you to file form 940.
If your business paid at least $1,500 in wages as mentioned above during either of those years, though, you’ll need to file form 940.
The only exception is if all of your employees are volunteers. In that case, you wouldn’t have been required to pay any federal payroll taxes on their behalf because they weren’t being compensated for their work.
In these circumstances, you don’t have to file a return. Instead, however, you must still provide each volunteer with a W-2 form at year-end.
You may also have to include an Employer Identification Number (EIN) box on W-2 forms filed with your state revenue department, but it varies by state.
The due date for filing Form 940 is January 31st but you get additional 10 calendar days if you deposit all of the FUTA tax when due.
How to file form 940 online?
The IRS allows taxpayers to e-file their tax returns by registering an account with E-File.gov.
Once your information has been verified, you will be able to file your taxes online. You can also request a copy of form 940 to mail-in by mail if you don’t have access to a computer or you can complete it using pen and paper.
Be sure to include all required information for each employee on the return when mailing it in. Make sure you are sending these forms through registered mail to ensure they arrive safely at their destination. If you are unable to find form 940 on any of these sites, call the IRS at 1-800-829-4933 for assistance with filing your employee taxes.
What is the difference between form 940 and 941?
The main difference between form 940 and form 941 has to do with employment taxes.
With form 941, you can pay your employees once a month; with form 940, you must wait until June 1st of each year.
So if you’re planning on keeping your employees on for multiple years, then go with form 941. If not, use form 940 because it simplifies tax payment options.
Note: even if you choose to use form 940, you still have to file information returns (such as forms W-2) by January 31st! Both forms cover Social Security and Medicare taxes, but form 940 includes income tax withholding.
Can I automate the entire process?
The good news for small business owners who need to submit quarterly tax payments is that, with today’s technology, you can automate your tax payments so you don’t have to worry about missing a deadline.
While it may be hard for some self-employed workers to track every 1099 they’ve received at year-end, payroll software such as UZIO will keep you on top of your forms and numbers.
Recommended reading: A Guide to Essential Payroll Forms & More for Small Business Owners
And we can help you pay those taxes quickly and easily, too. UZIO allows you to focus on your business and takes full control over how your payroll is processed and files taxes on your behalf without missing out on any due dates. UZIO allows employers to file their taxes online through their cloud-based payroll processing platform and deposit salaries in their employees’ bank account with just a few clicks.
Learn how UZIO is making life easier for small businesses.
Get an instructor-led demo with our payroll experts.
How to manage payroll when you are just starting out

Quick links
-
Decide the right structure for your business.
-
Get your Employer Identification Number (EIN).
-
Choose your tax period
-
Ensure your employees fill out the Form I-9 and Form W-4
-
Know your payroll taxes & file them as per the IRS guideline
-
File your payroll taxes on time
-
Find a full-service payroll solution to automate everything in the payroll process
Starting your own business can be incredibly rewarding, but if you’re not careful, it can also end up being extremely costly in terms of time and money. If you want to ensure that your startup succeeds in the long term, pay close attention to how you handle payroll when you’re just starting because when it comes to taxes and expenses, small businesses have some unique challenges to face. Take this guide on how to manage payroll in your early days as an entrepreneur to heart so that you don’t spend more than you need to in the coming years.
Decide the right structure for your business.
Before looking at how to do payroll, it’s a good idea to figure out what kind of business entity you’ll be. Is your business a sole proprietorship, a partnership, an LLC, or an S-corporation? Each has its own set of requirements and formalities. Sole proprietorships are easy to create and maintain, but they don’t provide as much liability protection as other forms. S-corporations offer more tax advantages and minimal personal liability, but setting one up requires additional filing procedures. Partnerships work well for small businesses with two or more owners sharing management tasks and profits. Corporate structures allow a company to take on a legal identity apart from its owners—an important consideration if your business operates internationally.
Get your Employer Identification Number (EIN).
Your EIN will be your business’s social security number, so to speak. It is essentially a taxpayer identification number for your company, which you will need if you hire employees. EIN is also called the Federal Tax Identification number that identifies your business. You can find information on obtaining an EIN at the IRS website. You can even apply for your EIN online here. Once obtained, keep it in a safe place because you will need it for all tax and financial transactions related to your business.
Choose your tax period
A business can choose how frequently it pays its taxes. Most businesses choose a monthly or quarterly period, but there are benefits to choosing a biweekly tax period. A business with lots of small transactions may save money by choosing an annual tax period because they won’t have to make as many estimated payments. However, if your business is seasonal and expects few sales in December, you might want to choose quarterly over annual if your sales typically peak in June. Keep in mind that whichever method you choose for your first year will be considered a permanent selection going forward, so be sure it’s right for your business from the start.
Ensure your employees fill out the Form I-9 and Form W-4
For a company to hire an employee, they need to provide certain information about themselves. One of these requirements is that employees provide their employer with a completed I-9 or Employment Eligibility Verification form. This form documents that employees are legally eligible for employment in America and can begin working. Employers should also have all employees fill out a W-4 form, which informs employers how much federal income tax they need to withhold from their paychecks. It’s important to know that even if an employee does not intend on filing taxes at the end of the year, they still must submit a filled-out W-4 so your company knows how much money should be withheld each pay period. This makes it easier for them to file taxes at year’s end since there won’t be any surprises. You can download Form I-9 and Form W-4 here directly by clicking on them.
Know your payroll taxes & file them as per the IRS guideline
Your payroll & employment taxes include the following:
- Social security and Medicare taxes
- Federal income tax withholding
- Federal unemployment tax (FUTA)
When your business is growing, likely, you’ll also be hiring more employees. As an employer, you must stay on top of all payroll taxes. First off, be sure to know what types of taxes are required for your business including federal, state & local taxes; for example, if you’re based in Texas and run a small company with five employees, you will need to pay state unemployment insurance (SUI), federal unemployment insurance (FUTA), and Medicare (HI) taxes. Additionally, as self-employed individuals, you and your employees may need to pay estimated quarterly taxes throughout the year. And don’t forget those other necessary forms: Form W-2 and Form 1099 for wages paid to employees and contractors/independent workers respectively.
File your payroll taxes on time
You can do it yourself or hire a professional to do it for you. There are chances of errors and data discrepancies if you do it yourself and the consequences of which could be severe, and result in high penalties, distrust amongst the employees, and would eventually consume tons of time to rectify the mistake. Alternatively, you can hire a professional to do so but even then you can’t be 100% sure as after all the professional you have outsourced to is only a human. Besides, hiring an external professional to manage your payroll can be expensive. Whatever you do, make sure you have the best resources available to file your payroll taxes on time.
Find a full-service payroll solution to automate everything in the payroll process
UZIO is a full-service payroll platform where business owners can run payroll with just a few clicks. The UZIO state-of-the-art solution ensures it is updated with the latest compliance and tax laws, to ensure a smooth and error-free process. UZIO is a self-service platform that allows your employees to view their pay stubs and get access to UZIO’s free customer service. The UZIO payroll solution can be ten times cheaper than outsourcing to a professional who still might be using UZIO or a platform similar to this for managing your payroll.
Get in touch with one of our payroll experts to schedule a demo today.